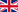
Coccinella septempunctata, the seven-spot ladybird (or, in North America, seven-spotted ladybug or "C-7"), is the most common ladybird in Europe. Its elytra are of a red colour, but punctuated with three black spots each, with one further spot being spread over the junction of the two, making a total of seven spots, from which the species derives both its common and scientific names (from the Latin septem = "seven" and punctus = "spot"). An adult seven-spot ladybird may reach a body length of 7.6–10.0 mm (0.3–0.4 in). Their distinctive spots and attractive colours apparently make them unappealing to predators. The species can secrete a fluid from joints in their legs which gives them a foul taste. A threatened ladybird may both play dead and secrete the unappetising substance to protect itself. The seven-spot ladybird synthesizes the toxic alkaloids, N-oxide coccinelline and its free base precoccinelline; depending on sex and diet, the spot size and coloration can provide some indication of how toxic the individual insect is to potential predators.
(latin: Coccinella septempunctata)