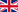
The song thrush (Turdus philomelos) is a thrush that breeds across much of Eurasia. It has brown upper-parts and black-spotted cream or buff underparts and has three recognised subspecies. Its distinctive song, which has repeated musical phrases, has frequently been referred to in poetry.
The song thrush breeds in forests, gardens and parks, and is partially migratory with many birds wintering in southern Europe, North Africa and the Middle East; it has also been introduced into New Zealand and Australia. Although it is not threatened globally, there have been serious population declines in parts of Europe, possibly due to changes in farming practices.
The song thrush builds a neat mud-lined cup nest in a bush or tree and lays four to five dark-spotted blue eggs. It is omnivorous and has the habit of using a favourite stone as an "anvil" on which to break open the shells of snails. Like other perching birds (passerines), it is affected by external and internal parasites and is vulnerable to predation by cats and birds of prey.
The song thrush (as represented by the nominate subspecies T. p. philomelos) is 20 to 23.5 centimetres (8 to 9.25 in) in length and weighs 50–107 grammes (1.8 to 3.8 oz). The sexes are similar, with plain brown backs and neatly black-spotted cream or yellow-buff underparts, becoming paler on the belly. The underwing is warm yellow, the bill is yellowish and the legs and feet are pink. The upperparts of this species become colder in tone from west to east across the breeding range from Sweden to Siberia. The juvenile resembles the adult, but has buff or orange streaks on the back and wing coverts.
The most similar European thrush species is the redwing (T. iliacus), but that bird has a strong white supercilium, red flanks, and shows a red underwing in flight. The mistle thrush (T. viscivorus) is much larger and has white tail corners, and the Chinese thrush (T. mupinensis), although much more similar in plumage, has black face markings and does not overlap in range.
The song thrush has a short, sharp tsip call, replaced on migration by a thin high seep, similar to the redwing's call but shorter. The alarm call is a chook-chook becoming shorter and more strident with increasing danger. The male's song, given from trees, rooftops or other elevated perches, is a loud clear run of musical phrases, repeated two to four times, filip filip filip codidio codidio quitquiquit tittit tittit tereret tereret tereret, and interspersed with grating notes and mimicry. It is given mainly from February to June by the Outer Hebridean race, but from November to July by the more widespread subspecies. For its weight, this species has one of the loudest bird calls.
An individual male may have a repertoire of more than 100 phrases, many copied from its parents and neighbouring birds. Mimicry may include the imitation of man-made items like telephones, and the song thrush will also repeat the calls of captive birds, including exotics such as the white-faced whistling duck.
The song thrush is omnivorous, eating a wide range of invertebrates, especially earthworms and snails, as well as soft fruit and berries. Like its relative, the blackbird, the song thrush finds animal prey by sight, has a run-and-stop hunting technique on open ground, and will rummage through leaf-litter seeking potential food items.
Land snails are an especially important food item when drought or hard weather makes it hard to find other food. The thrush often uses a favorite stone as an "anvil" on which to break the shell of the snail before extracting the soft body and invariably wiping it on the ground before consumption. Young birds initially flick objects and attempt to play with them until they learn to use anvils as tools to smash snails. The nestlings are mainly fed on animal food such as worms, slugs, snails and insect larvae.
(latin: turdus philomelos)